Home Tips & Tricks
Tips & Tricks Excel Functions
Excel Functions Excel Formulas
Excel Formulas Applied Formulas
Applied Formulas Applied Functions
Applied Functions Excel Macros
Excel Macros Business Uses
Business Uses Downloads
Downloads Excel Tests
Excel Tests Latest Updates
Latest Updates Recent Posts
Recent Posts About us
About us Q&A
Q&A
Compare Actual with Target in Pivot Table
[tcb-script async=”” src=”https://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/js/adsbygoogle.js”][/tcb-script][tcb-script] (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});[/tcb-script]
Comparing Actual with Target in Pivot Table always shows up the flaw of Pivot Table. Pivot Table can never do a good job because of the different sizes of the data set between Actual and Target numbers. However, with the launch of Power Pivot, this flaw no longer exist. This is because Power Pivot provided 2 useful features that Pivot Table does not have, combining 2 sets of data together without VLOOKUP and creating formulas within Pivot Table. If you have never heard of Power Pivot before, try
googling to find out what it is. We are not going to cover it here. Instead, I am going to jump right in and show you how to prepare the actual vs target in pivot table.
1. Download the working files here.
2. Go to the Actual worksheet.
3. Convert the data into an Excel Table.
4. Rename the Excel Table as Act.
5. Go to the PowerPivot tab and click on the “Create Link Table” icon. The data will be upload into the PowerPivot window as Act Table.
6. Go to the Target worksheet.
7. Convert the data into another Excel Table.
8. Rename the Excel Table as Tgt.
9. Go to the PowerPivot tab and click on the “Create Link Table” icon. The data will be upload into the PowerPivot window as Tgt Table.
10. Go to the Calendar worksheet.
11. Convert the data into another Excel Table
12. Name this table as Cal.
13. Go to the PowerPivot tab and click on the “Create Link Table”icon. The data will be upload into the PowerPivot window as Cal Table.
13. Go to the PowerPivot tab and click on the “Create Link Table” icon. The data will be upload into the PowerPivot window as Cal Table.
14. In the PowerPivot tab, click on the first icon “PowerPivot window”. You will be brought to the PowerPivot Window.
14. In the PowerPivot tab, click on thefirst icon “PowerPivot window”. You will be brought to the PowerPivotWindow.
15. In the PowerPivot window, click on the icon “Diagram View”located near the end of the Ribbon.
15. In the PowerPivot window, clickon the icon “Diagram View” located near the end of the Ribbon.
16. Create 3 columns, one in each table by combining the Year and theMonth column together. The formula for the Act Table should be =year(Act[Invoice Date])*100+MONTH(Act[Invoice Date]). The column name is PeriodID.
16. Create 3 columns, one in eachtable by combining the Year and theMonth column together. The formulafor the Act Table should be =year(Act[Invoice Date])*100+
MONTH(Act[Invoice Date]). The column name is PeriodID.
17. For the other 2 tables, replace the Table name and the column namesin the formula.
17. For the other 2 tables, replace theTable name and the column namesin the formula.
18. Link the 3 tables together by dragging the “Invoice Date” columnin the Act Table to the “Date” column in Cal Table. Create a date column called TDate for Tgt Table by using the Date formula =DATE(Tgt[Year],Tgt[MonthNo],1) and drag the “TDate” column in TgtTable to the “Date” in the Cal Table.
18. Link the 3 tables together bydragging the “Invoice Date” column in the Act Table to the “Date” column in Cal Table. Create a date column called TDate for Tgt Table by usingthe Date formula =DATE(Tgt[Year],Tgt[MonthNo],1)and drag the “TDate” column in TgtTable to the “Date” in the Cal Table.
19. Go back to the Excel window. In the PowerPivot tab, click on the PivotTable. The Pivot Table created is different from the Pivot Table fromthe Insert tab.
19. Go back to the Excel window. Inthe PowerPivot tab, click on the PivotTable. The Pivot Table created isdifferent from the Pivot Table fromthe Insert tab.
20. In the PowerPivot tab, click on the icon “New Measure” and Sum up theAmount in the Act Table.
20. In the PowerPivot tab, click on theicon “New Measure” and Sum up theAmount in the Act Table.
21. Create another measure called Target Sales and enter the followingDAX formula into the measure =CALCULATE(SUM(Tgt[Target]),FILTER(ALL(Tgt[PeriodID]),CONTAINS(VALUES(Cals[PeriodID]), Cals[PeriodID],Tgt[PeriodID])),
21. Create another measure calledTarget Sales and enter the followingDAX formula into the measure=CALCULATE(SUM(Tgt[Target]),FILTER(ALL(Tgt[PeriodID]),CONTAINS(VALUES(Cals[PeriodID]),Cals[PeriodID],Tgt[PeriodID])),
FILTER(ALL(Tgt[Name]),CONTAINS(VALUES(Act[Slsman]),Act[Slsman],Tgt[Name])))
FILTER(ALL(Tgt[Name]),CONTAINS(VALUES(Act[Slsman]),Act[Slsman],Tgt[Name])))
22. Drag the Name into the Row Label box and the Actual Month into the Column Label box and your report will be able to align the Actual Sales with the Target Sales.
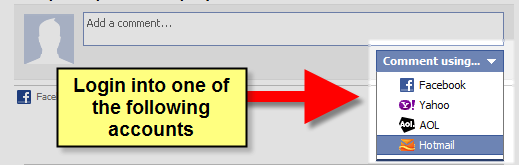
New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.
Share this page:
Enjoy this page? Please pay it forward. Here’s how…
Would you prefer to share this page with others by linking to it?
- Click on the HTML link code below.
- Copy and paste it, adding a note of your own, into your blog, a Web page, forums, a blog comment, your Facebook account, or anywhere that someone would find this page valuable.
<a href=”http://www.advanced-excel.com/”>Advanced Excel – From a Business Perspective</a><a href=”http://www.advanced-excel.com/”>Advanced Excel – From a Business Perspective</a>

Excel Courses for Business Professionals
Copyright © advanced-excel.com 2007 – 2019. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
Microsoft® and Microsoft Excel® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
advanced-excel.com is in no way associated with Microsoft